Central to the success of hybrid QM/QM models is the assumption that the system can be divided into two regions: (1) a small region where interesting chemistry occurs and a very accurate model chemistry is needed; (2) the surrounding region composed of the rest of the atoms where a less accurate model chemistry will suffice. Unlike most previous approaches, we are developing techniques where the electronic environment from the surroundings contributes explicitly to the electronic structure of the key central region. This electronic embedding
model leads to an economical and accurate theoretical description, and enables us to accurately model large molecules and materials. Among the approaches currently underway are:
Point Charge/Density Embedding
By inserting a Region I-derived potential into the Region II Hamiltonian, the high level wavefunction is explicitly polarized by either quantum mechanical atomic charges or the actual electron density of the low level region.
Charge Transfer
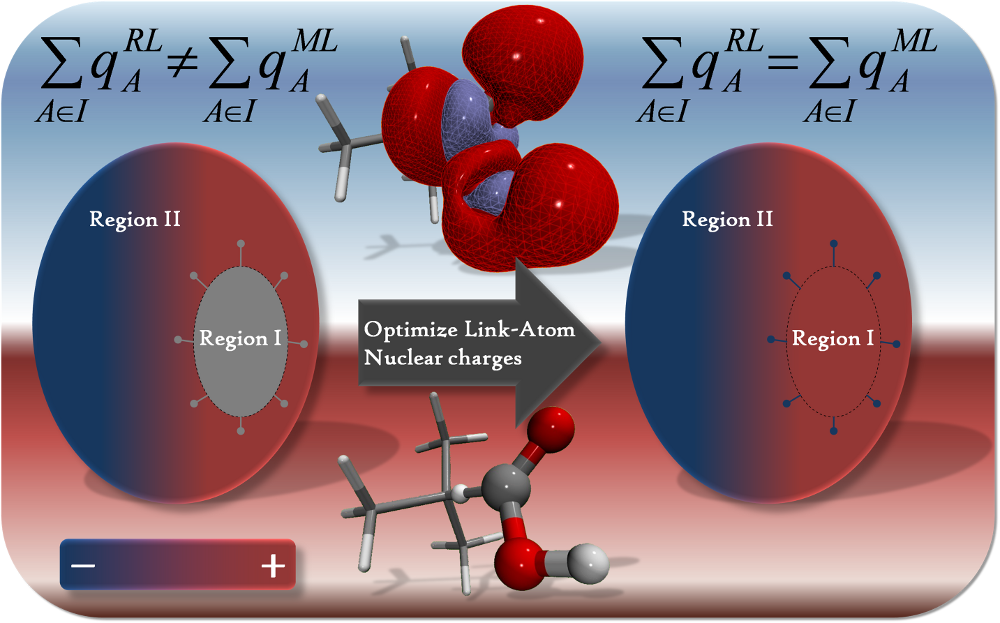
All ONIOM-based methods suffer from problems related to neglecting charge redistribution. When a molecule is divided into separate sub-systems, each new region is required to assume an integer number of electrons. We are currently working on several approaches to account for the charge-transfer across the regional divide. Among these approaches is the development of a constrained SCF method which may be used to constrain regional atomic charges.
Applications
A variety of applications using our new electronic embedding approaches are being carried out. The applications include chemical reactions on semiconductor surfaces, metal-oxide surfaces with applications to dye-sensitized solar cells, and new models to describe solvation effects and biomolecular interactions.